
In a TCP/IP network, the loopback IP address is 127.0. How does a loopback address work?Īn address that sends outgoing signals back to the same computer for testing. They help to select, designated router and Backup Designated router when the routing protocol OSPF is configured in the network. The loopback address is used by OSPF as router ID to stabilize the process. The loopback address is used to access the router for management. Read More: What is the driving force for the Hadley cell circulation What is the purpose of a loopback address on a router? The address is used to establish an IP connection to the same machine or computer being used by the end-user.

0.1 is the loopback Internet protocol (IP) address also referred to as the localhost. What is loopback IP address 127.0 0.1 indicates?ġ27.0. Loopback interface’s IP Address determines a router’s OSPF Router ID. A loopback interface is not a physical interface like Fast Ethernet interface or Gigabit Ethernet interface. What is loopback IP in router?Ī loopback interface is a logical, virtual interface in a Cisco Router. 0.1 will be assigned to a special interface on your host, the loopback interface, which acts like a closed circuit. 0.0 is reserved for IP traffic local to your host. What is the purpose of 127.0 0.0 IP address? This can be used for diagnostic purposes to verify that the internal path through the TCP/IP protocols is working. Packets sent to this address never reach the network but are looped through the network interface card only.
Unix-like systems usually name this loopback interface lo or lo0. The IPv6 loopback address corresponds to 127.0. Various Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standards reserve the IPv4 address block 127.0.0.0/8, in CIDR notation and the IPv6 address ::1/128 for this purpose. Loopback IP address is managed entirely by and within the operating system. These addresses enable the Server and Client processes on a single system to communicate with each other. When a process creates a packet with destination address as loopback address, the operating. The most common IPv4 address used is 127.0.0.1. Moreover, which prefix length is most appropriate for an IPv6 loopback address?įor IPv4, this address is 127.0.
For the new larger loopback prefix, the address automatically configured on the loopback interface should be: 1::1/64. Similarly, what is IPv4 loopback? A “ loopback” is an address that causes the traffic to be sent to the same interface is was sent out on on the localhost. Usage of loopback addresses are particularly popular with developers and anyone in IT performing network tests. Likewise, people ask, what is IPv6 used for?, then perform one of the following steps to specify a static IP address and network mask for the interface.įor instance, if you think your Network Card is failing you can try: PING 127.0.0.1. Enter an IPv4 address with a subnet mask of /32 for example, 192.168.2.1/32. Internet Protocol Version 6 ( IPv6) is a network layer protocol which allows communication and data transfers to take place over the network. Here you can find all lookup results for loopback IP address 127.1.1.1 which is located in 127.0.0.0/8, a reserved range for loopback addresses to the local host (RFC 6890).

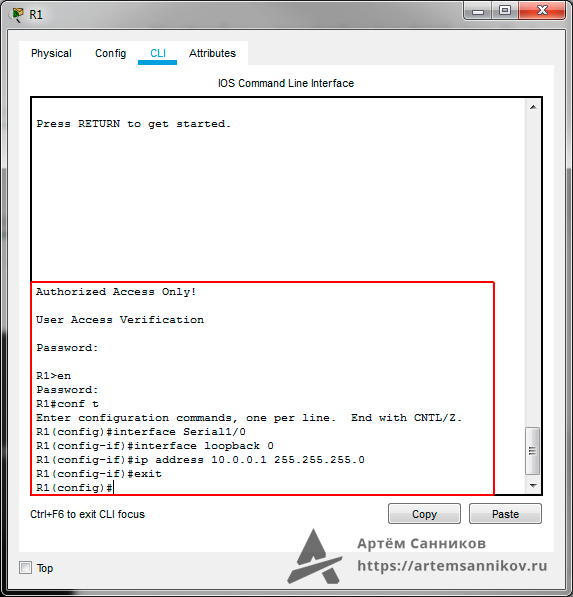
IPv6 came into existence in 1998 with the sole purpose to take over and replace IPv4 protocol one day. IP address 127.1.1.1 is registered as a loopback interface address, which is also known as localhost or local host. In computer networking, localhost is a hostname that. A loopback interface is a virtual interface in our network device that is always up and active after it has been configured. Typically, link-local IPv6 addresses have “ FE80” as the hexadecimal representation of the first 10 bits of the 128-bit IPv6 address, then the least-significant 64-bits of the address are the Interface Identifier (IID). Like our physical interface, we assign a special IP address which is called a loopback address or loopback IP address. Loopback interfaces should be supported on all Cisco platforms, and unlike subinterfaces, loopback.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
